Section 2.4: Basic Constructions of Lasers
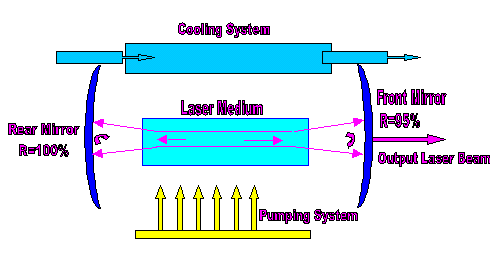
Figure 2.2: A basic laser system
A basic laser system (see figure above) has two mirrors that are placed parallel to each other to form an optical oscillator so that light can be transmitted back and forth between the mirrors along the optical axis. Between the mirrors is the active medium that can amplify the light by stimulated emission. Under certain pumping mechanism, the active medium can be excited from lower energy state to upper energy state, population inversion happens. Stimulated emissions give out photons in all directions at first. But the photons are transmitted through the system, only photons whose directions are along the optical axis can last, photons in other directions will either be scattered or absorbed. Soon almost all the photons in the system are oscillating in the optical axis direction. One incident photon can become two photons after every stimulated emission, so under proper conditions, light density is amplified. Usually one of the mirrors is nearly totally reflecting, another is partially reflecting, the partially reflecting mirror will output laser light either in continuous wave (CW) or in pulse. Working laser may give out a lot of heat, this heat can affect the operation quality seriously. So lasers usually have cooling systems.
You can try the Laser System Demo to know how to build a Basic Laser System. Click on the following link below.
G2.3: Laser System Demonstration
![]() if you
can not run this animation properly,you should download MacroMedia Shockwave
from http://www.macromedia.com/shockwave/download/
if you
can not run this animation properly,you should download MacroMedia Shockwave
from http://www.macromedia.com/shockwave/download/
The optical mirrors, active medium and pumping system form the laser resonator, which is also called Laser Cavity. Laser cavities can be divided into Stable Cavities and Unstable Cavities according to whether they make the oscillating beam converge into the cavity or spread out from the cavity. Normal power lasers (<2kW) commonly use stable cavity designs. Under normal powers, the mirrors are safe to transmit the laser in the cavity and couple it out. Stable cavities have the advantage of continuous central beam intensity distribution and good property for focusing. But when laser power is very high, the risk of mirror breakage increases, unstable cavities are commonly used. Unstable cavity has ring shaped output beam, the beam comes out from around the edge of the output mirror. Click to see details on various laser resonators.